The Japanese Pharmacopoeia (JP) is an official document that defines the specifications, criteria and standard test methods necessary to properly assure the quality of medicines in Japan.
Paragraph 2, Article 41 of the Law on Securing Quality, Efficacy and Safety of Products including Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices stipulates that
full-fledged JP revisions shall be presented at least every 10 years. Since the JP 9th edition, full-fledged revisions have been made every 5 years. In addition to
the full-fledged revisions, a supplement has been promulgated twice in every 5 years since the JP 12th edition as well as partial revisions have been made as necessary to take account of recent progress of science and in the interests of international harmonization.
The 16th Edition of the JP was promulgated by Ministerial Notification No. 65 of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) on March 24, 2011. In July 2011, the Committee on JP established the basic principles for the preparation of the JP 17th Edition, setting out the roles and characteristics of the JP, the definite measures for the revision, and the date of the revision.
the JP 17th Edition carries 1962 articles, owing to the addition of 76 articles and the deletion of 10 articles
The JP 17th Edition comprises the following items, in order: Notification of MHLW; Contents; Preface; General Notices; General Rules for Crude Drugs; General Rules for Preparations; General Tests, Processes and Apparatus; Official Monographs; then followed by Infrared Reference Spectra and Ultraviolet-visible Reference Spectra; General Information; Table of Standard Atomic Weights as an appendix; and a Cumulative Index
The articles in Official Monographs, Infrared Reference Spectra and Ultraviolet-visible Reference Spectra are respectively placed in alphabetical order in principle.
The following items in each monograph are put in the order shown below, except that unnecessary items are omitted depending on the nature of the drug:
(1) English title
(2) Commonly used name(s)
(3) Latin title (only for crude drugs)
(4) Title in Japanese
(5) Structural formula or empirical formula
(6) Molecular formula and molecular mass
(7) Chemical name
(8) Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Registry Number
(9) Origin
(10) Limits of the content of the ingredient(s) and/or the unit of potency
(11) Labeling requirements
(12) Method of preparation
(13) Manufacturing requirement
(14) Description
(15) Identification tests
(16) Specific physical and/or chemical values
(17) Purity tests
(18) Potential adulteration
(19) Loss on drying or Ignition, or Water
(20) Residue on ignition, Total ash or Acid-insoluble ash
(21) Tests being required for pharmaceutical preparations
(22) Other special tests
(23) Assay
(24) Containers and storage
(25) Shelf life
(26) Others
In each monograph, the following physical and chemical values representing the properties and quality of the drug are given in the order indicated below, except that unnecessary items are omitted depending on the nature of drug:
(1) Alcohol number
(2) Absorbance
(3) Congealing point
(4) Refractive index
(5) Osmolar ratio
(6) Optical rotation
(7) Constituent amino acids
(8) Viscosity
(9) pH
(10) Content ratio of the active ingredients
(11) Specific gravity
(12) Boiling point
(13) Melting point
(14) Acid value
(15) Saponification value
(16) Ester value
(17) Hydroxyl value
(18) Iodine value
Identification tests comprise the following items, which are generally put in the order given below:
(1) Coloration reactions
(2) Precipitation reacti0ons
(3) Decomposition reactions
(4) Derivatives
(5) Infrared and/or ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrometry
(6) Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry
(7) Chromatography
(8) Special reactions
(9) Cations
(10) Anions
Purity tests comprise the following items, which are generally put in the order given below, except that unnecessary items are omitted depending on the nature of drug:
(1) Color
(2) Odor
(3) Clarity and/or color of solution
(4) Acidity or alkalinity
(5) Acidity
(6) Alkalinity
(7) Chloride
(8) Sulfate
(9) Sulfite
(10) Nitrate
(11) Nitrite
(12) Carbonate
(13) Bromide
(14) Iodide
(15) Soluble halide
(16) Thiocyanate
(17) Selenium
(18) Cationic salts
(19) Ammonium
(20) Heavy metals
(21) Iron
(22) Manganese
(23) Chromium
(24) Bismuth
(25) Tin
(26) Aluminum
(27) Zinc
(28) Cadmium
(29) Mercury
(30) Copper
(31) Lead
(32) Silver
(33) Alkaline earth metals
(34) Arsenic
(35) Free phosphoric acid
(36) Foreign matters
(37) Related substances
(38) Isomer
(39) Optical isomer
(40) Multimers
(41) Residual solvent
(42) Other impurities
(43) Residue on evaporation
(44) Readily carbonizable substances
The following paragraphs were newly added to General Notices:
(1) Paragraph 12: The item ``Manufacturing requirement'' was newly added in monograph in order to specify the requirements that should be noted on manufacturing processes such as control of intermediates and manufacturing processes.
(2) Paragraph 34: The specification for residual solvents was added.
(3) Paragraph 35: The item ``Potential adulteration'' was added in monograph in order to describe control of harmful substances that was intentionally contaminated.
(4) Paragraph 40: The definitions of ``sterility'', ``sterilization'' and ``aseptic technique'' as sterility related terms were added.
8. The following paragraphs of General Notices
were revised:
(1) Paragraph 5: Container under ``Containers and
storage'' for preparations (excluding preparations containing crude drugs as main active ingredients) in the monographs were removed
from the standards for conformity.
(2) Paragraph 48: The symbols ( ) were newly added as the ways to indicate the part being not harmonized among three pharmacopoeias in order to distinguish ``JP local requirements'' from ``non-harmonized attributes/provisions among three pharmacopoeias''.
(3) Other descriptions were improved.
To Paragraph 1 of General Rules for Crude
Drugs the following items were added:
(1) Codonopsis Root
(2) Hedysarum Root
(3) Salvia Miltiorrhiza Root
JAPANESE PHARMACOPOEIA 17 DOWNLOAD LINK
JAPANESE PHARMACOPOEIA SUPPLIMNET 1
JAPANESE PHARMACOPOEIA SUPPLIMNET 2




.JPG)











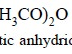

![Difference between Stability[Shelf life] Specification and Release Specification](https://4.bp.blogspot.com/-O3EpVMWcoKw/WxY6-6I4--I/AAAAAAAAB2s/KzC0FqUQtkMdw7VzT6oOR_8vbZO6EJc-ACK4BGAYYCw/w680/nth.png)
0 Comments